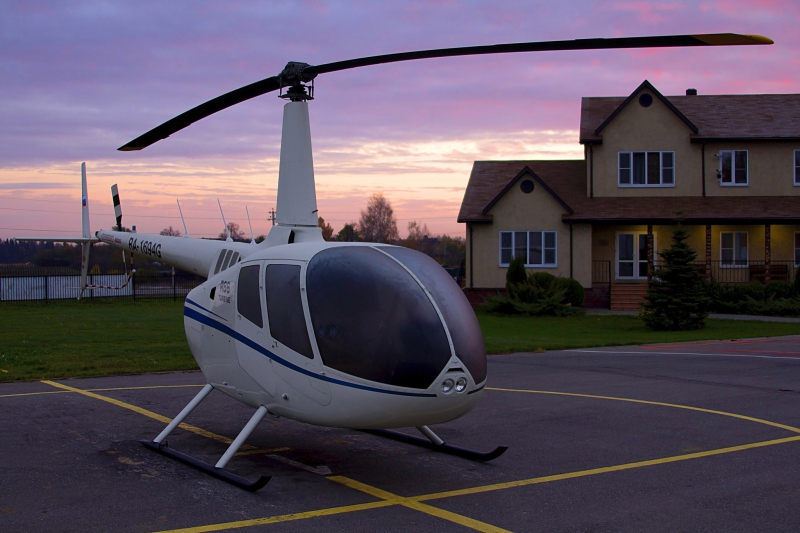
Single engine helicopter Robinson R66, equipped with the additional fuel tanks, navigation systems, survival kit and equipment for professional shooting and video recording will be expedition’s only transportation means along the borders of the Russian Federation.
R66 Turbine is the first gas-turbine helicopter made by Robinson Helicopter Company. Mass production started in 2010. Gas-turbine engine was developed for this model exclusively by British Company Rolls-Royce.
R66 Turbine has a lot of features of the previous model R44, including biblade carrier system, T-shaped cyclic pitch knob, and cab’s configuration. The main differences are increased reserve power, updated altitude performance, fifth passenger’s seat, xenon’s landing lamp together with LED ANO and spacious luggage boot, which during expedition will be taken by the additional fuel tanks.
Technical features of the expidition’s aircraft (R66, RA-1694G):
General features:
- Total length: 11.66 m
- Rotor’s diameter: 10.06 m
- Total height: 3.48 m
- Empty craft mass: 581 kg
- Allowed take-off weight: 1225 kg
- Engine: 1 x Rolls-Royce RR300, turboprop, 300 horsepower
Specific features:
- Max speed: 259 km/h (161 miles/h)
- Cruise speed: 222 km/h (138 miles/h)
- Maximum distance: 1000 km
- Max height: 4270 m
- Average fuel consumption rate: 90 l/h
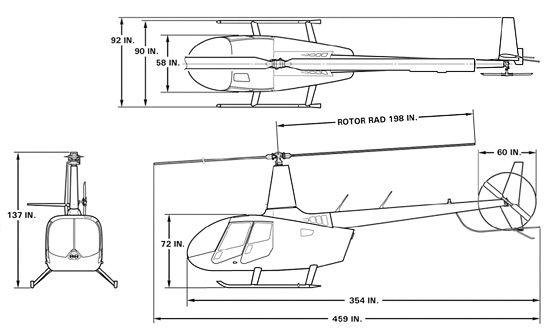
dimensions
Equipment for the expedition’s helicopter (R66, RA-1694G):
- Supervision system hydraulic boost system
- Cabin heat and ventilation system
- Antiglare toning of the windscreen
- Removable set of second control box
- Adjustable footplate
- Lifting propeller’s brakes
- Leather seats
- Inner touch-up by carpet mat
- Noise insulation
- Luggage lofts under seats
- Luggage loft with highlighting
- Aircraft’s bottom is hardened
- Xenon landing lights HID
- LED landing lights
- Highlight of the control panel
- Navigational highlight
- Reel-to-reel inertial safety belts
- Ground service wheels
- Windscreen cover and blade lashings
- Vertical speed indicator
- Aerial (dash) speed indicator
- Rotor’s and engine’s dual tachometer
- Anemometerial altimeter (pressure-based)
- Radio altimeter
- Magnetic compass
- Gyroscopic semi-compass
- Turbo-propeller compressor’s tachometer
- Torque’s index
- Aeronautical VHF radio communicator King KY 196A COM, 2 sets
- Transponder (receiver) Garmin GTX 327, Mode S
- Audio panel VOX, NAT AA 12S-600
- DVD-player and AM / FM radio
- Floor and manual switches of the intercoms
- Quartz watch
- Digital meter of the outdoor temperature
- Engine’s life counter and flight hours counter
- Digital voltmeter
- Temperature sensor of the gas inside the turbine
- Oil temperature and pressure indicator
- Built-in oil filter with the passageway indicator
- Air engine filter with the passageway indicator
- Starter Generator 160 A
- Electronic system of the engine monitoring
- Built-in alerts indication panel
- GPS-navigator Garmin 495 (route and main navigational characteristics)
- GPS-navigator Garmin 695 (moving map and flight’s plan)
- GPS-navigator Garmin 795 (map, flight’s plan, flight’s altitude profile)
- Satellite tracker SPOT-2 (search and rescue guarantee)
- Satellite tracker Yellow Brick (on-line flight’s tracking, emergency communications, search and rescue)
- Satellite tracker DeLorme InReach (on-line flight’s tracking, emergency communications, search and rescue)
- Satellite cellphone Iridium 9575 extreme (phone communication)
- Satellite terminal Iridium AxcessPoint (low-speed Internet connection)
- Satellite terminal Inmarsat BGAN Hughes 9202 (high-speed Internet connection)
- Protection helmets MCA with in-build communication tools – 2 sets
- Navigational iPAD-3 (reserve navigation, text messages exchange)
- Navigational iPAD-4 (surveying route maps, scale – 2 km (1.24 miles))
- Electronic Cartography Acer Iconia Tab W510c (aviation maps along the route, spacing – 2 km)
- Radio set for aviation USB-communications Vertex Standart VXA-710 (reserved)
pictures
Aircraft’s advantages: The possibility of landing on almost any open area of the small size. High flexibility to respond to the deterioration of weather conditions: the ability to wait out bad weather or reduce the height and speed to overcome the bad weather. Much bigger opportunities for the decision-making in case of the engine failure. During forced landing, in case of the good autorotation technique, helicopter’s and crew’s safety is guaranteed with high possibility. In general, during forced landing, chances of survival are higher (than in an airplane).
Aircraft’s disadvantages: Unstable aerodynamic design. During flight requires constant, every second maintenance of the equilibrium state, which leads to the pilot’s fatigue faster. For the same reason, is dangerous in a blind piloting, as it requires significant over-concentration and experience when flying on instruments; does not forgive mistakes. Due to these features, flying on instruments without special equipment is prohibited – only visual flight. Fuel consumption per hour is bigger, and the range is smaller. Has basic (aerodynamical) speed limits.


